Low iron and ferritin are among the most common deficiencies in both women and men. They manifest as fatigue, hair loss, weakness, shortness of breath, anxiety, and the inability to regain energy even after rest.
Ferritin is the body’s “iron bank.” When it is low, the body cannot properly produce hemoglobin, transport oxygen, or support the functioning of the thyroid gland, brain, muscles, and immune system.
Why ferritin drops
-
insufficient dietary iron intake
-
heavy menstruation
-
pregnancy and breastfeeding
-
low stomach acidity
-
gastritis, H. pylori, celiac disease
-
blood donation
-
veganism/vegetarianism
-
intensive training
-
chronic inflammatory conditions

Main symptoms of low ferritin
-
severe fatigue, apathy
-
hair loss, brittle nails
-
shortness of breath during exertion
-
rapid heartbeat
-
poor sleep
-
cold hands and feet
-
headache
-
anxiety
-
low stress tolerance
Table 1. Optimal values and what they mean
| Marker | Reference range | Optimal | What it means |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ferritin | W: 30–150 ng/ml, M: 50–200 | 60–100 | Iron stores in the body |
| Iron | 8–30 µmol/L | 15–25 | Amount circulating in the blood |
| Transferrin saturation | 20–45% | 30–40% | How efficiently the transport system works |
| Hemoglobin | W: >120, M: >130 | • | Late marker of deficiency, not informative at early stages |
| Vitamin B12 | >250 | 350–600 | Synergy with iron in erythropoiesis |
| Folate | >4 ng/ml | >8 | Important for red blood cell synthesis |
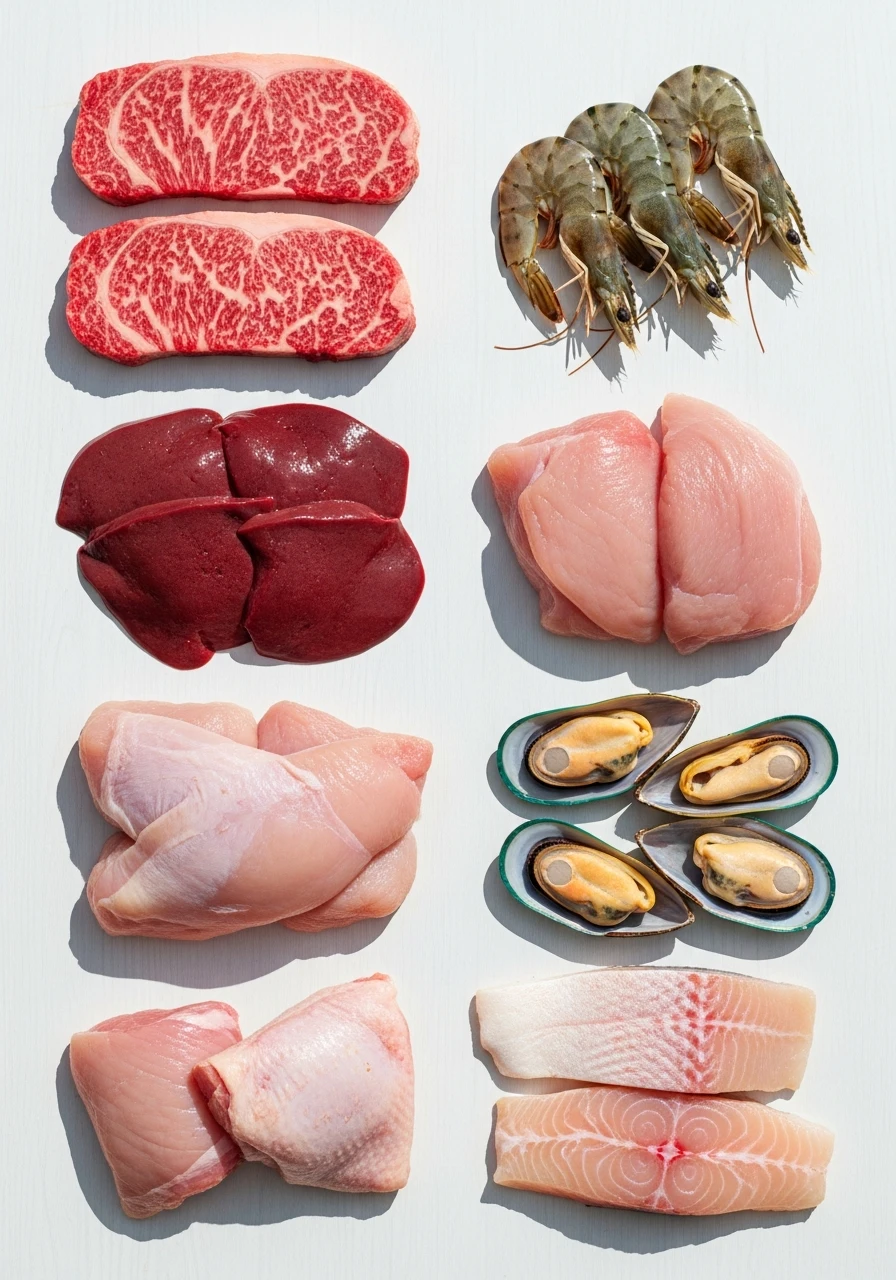
How to increase iron and ferritin: strategy
Nutrition
Heme iron (best absorbed)
-
beef
-
veal
-
turkey
-
liver
-
seafood
Non-heme iron
-
buckwheat
-
spinach
-
legumes
-
pumpkin seeds
-
beans
Absorption enhancers
-
vitamin C
-
lemon juice
-
fermented foods
Blockers (do not combine with iron intake)
-
coffee, black tea
-
dairy products
-
calcium
-
antacids
-
fiber (high doses)
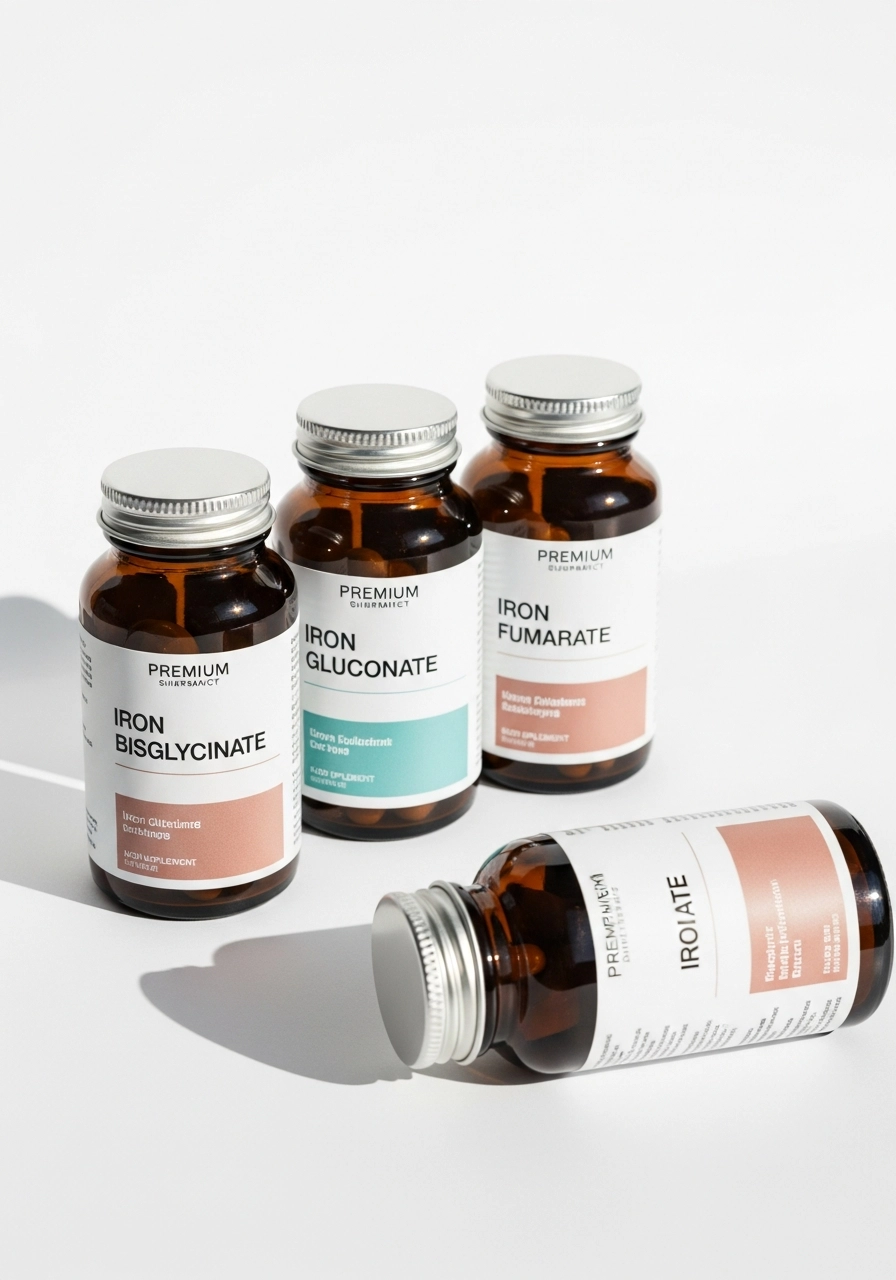
Iron supplements: how to choose the form
Best forms with high absorption
-
iron bisglycinate (chelate) — top choice, minimal side effects
-
iron gluconate — gentle form
-
iron fumarate — strong, may cause side effects
Dosages
-
ferritin <20 → 40–60 mg of elemental iron
-
ferritin 20–40 → 20–40 mg
-
ferritin 40–60 → 10–20 mg maintenance
Rules of intake
-
on an empty stomach or 1 hour before meals
-
take with water + 250 mg vitamin C
-
do not combine with coffee, dairy, calcium
Supporting nutrients
Vitamin C
Improves absorption by 2–3 times.
Vitamin B12 (methylcobalamin)
Low B12 = ferritin increases more slowly.
Folic acid (B9)
Essential for red blood cell synthesis.
Copper
Without it, iron is not incorporated into hemoglobin.
Zinc
Balance with copper for hematopoiesis.
Table 2. Nutrients, synergy, and why they are needed for iron and ferritin
| Nutrient | Role | When to add |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C | improves iron absorption | always when taking iron |
| B12 | red blood cell synthesis | low energy, vegetarians |
| Folate (B9) | hematopoiesis | pregnancy planning, anemia |
| Zinc + copper | trace element balance | hair loss, low ferritin |
| Probiotics | improved absorption | gastritis, bloating |
How long it takes to raise ferritin
-
first changes — after 4–6 weeks
-
ferritin increase — 2–4 months
-
deep deficiency — up to 6 months
-
after normalization: another 1–2 months of maintenance
Important: ferritin rises more slowly than iron and hemoglobin levels.
When intravenous iron is needed
-
ferritin <10
-
heavy menstruation
-
H. pylori, malabsorption
-
pregnancy with severe deficiency
-
inability to tolerate oral forms
Most common mistakes
-
taking iron with coffee → zero effect
-
stopping intake after 2–3 weeks
-
taking iron with calcium
-
choosing the wrong form
-
not treating the cause (menstruation, gastritis)
-
not checking B12 and folate
Conclusion
Raising iron and ferritin is achievable. It requires the right form of iron, consistency, enhancers (C, B12, folate), avoiding blockers, and addressing the root cause. Quality nutraceuticals can be purchased online at medizine.ua. Read more about health on our Blog.
After 1–2 months, energy improves, sleep gets better, and hair loss decreases.
After 3–4 months, ferritin stores normalize.
References
-
Tolkien Z. Efficacy of ferrous bisglycinate. Nutrients.
-
Camaschella C. Iron deficiency. New England Journal of Medicine.
-
WHO. Iron deficiency anemia guidelines.
-
Cepeda-Lopez A. Iron absorption and vitamin C. AJCN.
-
Otero-Losada M. Iron metabolism and inflammation. Frontiers in Physiology.