
Biotin (or vitamin B7) is a water-soluble vitamin that is actively involved in the body’s metabolic processes.
Biotin plays a key role in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins.

Recent studies have shown that biotin affects the regulation of genes related to glucose metabolism and may also improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of insulin resistance, making it an important element for maintaining normal blood sugar levels, especially in people with diabetes.

Biotin and its role in glucose metabolism
Biotin helps normalize blood glucose levels through its effect on enzymes involved in carbohydrate metabolism.
Biotin activates enzymes such as pyruvate dehydrogenase and acetyl-CoA carboxylase, which help the body convert carbohydrates into energy.
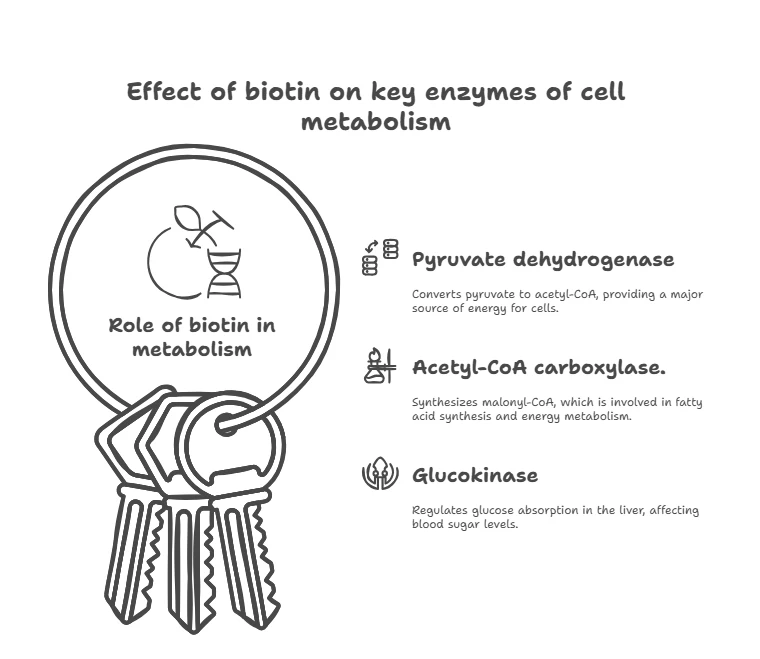
Table 1: Effect of biotin on enzymes of glucose metabolism
| Enzyme | Role in glucose metabolism | Effect of biotin |
|---|---|---|
| Pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) | Converts pyruvate to acetyl-CoA, the main source of energy for cells | Biotin activates this enzyme, improving the breakdown of carbohydrates in cells. |
| Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) | Synthesizes malonyl-CoA, which is involved in fatty acid synthesis and maintains energy balance | Biotin promotes ACC activity, helping to improve energy metabolism. |
| Glucokinase (GK) | Controls the rate of glucose uptake by liver cells | Biotin increases glucokinase activity, promoting better glucose absorption. |
This table shows how biotin affects the key enzymes that regulate glucose metabolism.
This is an important aspect for maintaining stable blood sugar levels, especially in people with diabetes.
Biotin and insulin resistance
Insulin resistance is a condition in which tissues lose the ability to utilize insulin effectively.
Biotin can affect insulin sensitivity through the regulation of genes responsible for insulin receptor synthesis.
Table 2: Effect of biotin on insulin resistance
| Research | Dose of biotin | Results |
|---|---|---|
| Metabolism, 2018 | 5 mg per day | Improving insulin sensitivity and lowering blood glucose levels. |
| J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2020 | 10 mg per day | Reducing inflammation and improving insulin sensitivity in prediabetic patients. |
| Diabetes Metab Syndr, 2021 | 2 mg per day | Improving pancreatic beta-cell function and normalizing blood sugar levels. |
This table describes the effects of different doses of biotin on insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism.
Given that insulin resistance is an important aspect in the development of type 2 diabetes, biotin supplementation may help prevent or slow the progression of this disease.
Biotin and regulation of genes related to glucose metabolism
Biotin regulates the activity of multiple genes that are responsible for the synthesis of insulin receptors and other key molecules involved in carbohydrate metabolism.
In particular, biotin affects the expression of genes that regulate blood sugar levels and insulin sensitivity.
Table 3: Genetic effects of biotin on glucose metabolism
| Gene | Effect of biotin | Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| GCK (Glucokinase) | Increases gene expression by stimulating glucose uptake | Biotin improves glucokinase activity, which promotes glucose uptake by cells. |
| IRS1 (Insulin Receptor Substrate 1) | Increases gene expression, helping to improve insulin sensitivity | Biotin activates genes that help improve insulin sensitivity. |
| PPAR-γ (Proliferator-activated receptor-γ). | Regulates lipid and carbohydrate metabolism | Biotin improves PPAR-γ expression, affecting fat metabolism and insulin sensitivity. |
This table shows how biotin affects the expression of genes that are involved in glucose metabolism.
This effect may be beneficial for people with disorders of carbohydrate metabolism such as diabetes or metabolic syndrome.

Conclusion
Biotin plays an important role in normalizing glucose metabolism and improving insulin sensitivity.
Regular consumption of biotin can significantly affect blood sugar levels, which has implications for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Current research confirms its positive effect on metabolic processes, and further studies will help to reveal the full picture of its effects.
List of references:
- J Nutr Biochem, 2019. “Role of biotin in glucose metabolism.”
- Metabolism, 2018. “Effect of biotin supplementation on insulin sensitivity.”
- Diabetes Metab Syndr, 2020. “Impact of biotin on insulin secretion in diabetic patients.”
- J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2021. “Biotin supplementation improves insulin sensitivity in prediabetes.”




