
Choline is an important organic compound that plays a key role in lipid metabolism and the maintenance of normal liver function.
Although often underestimated, choline is essential for the synthesis of phospholipids such as phosphatidylcholine, which make up cell membranes and are important for normal liver function.
In recent years, research has confirmed the importance of choline in the prevention of a number of liver diseases, including non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and cirrhosis.
In this article, let’s look at how choline affects liver health and why choline intake is important for disease prevention.

Role of choline in lipid metabolism
Choline is involved in lipid transport, especially in fat metabolism in the liver.
Recent studies show that choline deficiency can lead to fat accumulation in liver cells, which is one of the factors in the development of NAFLD (Zhao et al., 2019).
The synthesis of phosphatidylcholine, the main component of cell membranes, is impossible without choline. This process is necessary for normal metabolism of lipids in liver cells and their transport to other parts of the body.

Choline and the prevention of liver disease
Choline deficiency is strongly associated with the development of liver diseases such as NAFLD, cirrhosis, and even liver cancer.
Studies have shown that increasing choline intake can reduce fat accumulation in the liver and reduce inflammation, which contributes to protection against these diseases (Yang et al., 2021).
Of particular note is that choline affects the metabolic pathways that prevent fat accumulation in the liver.

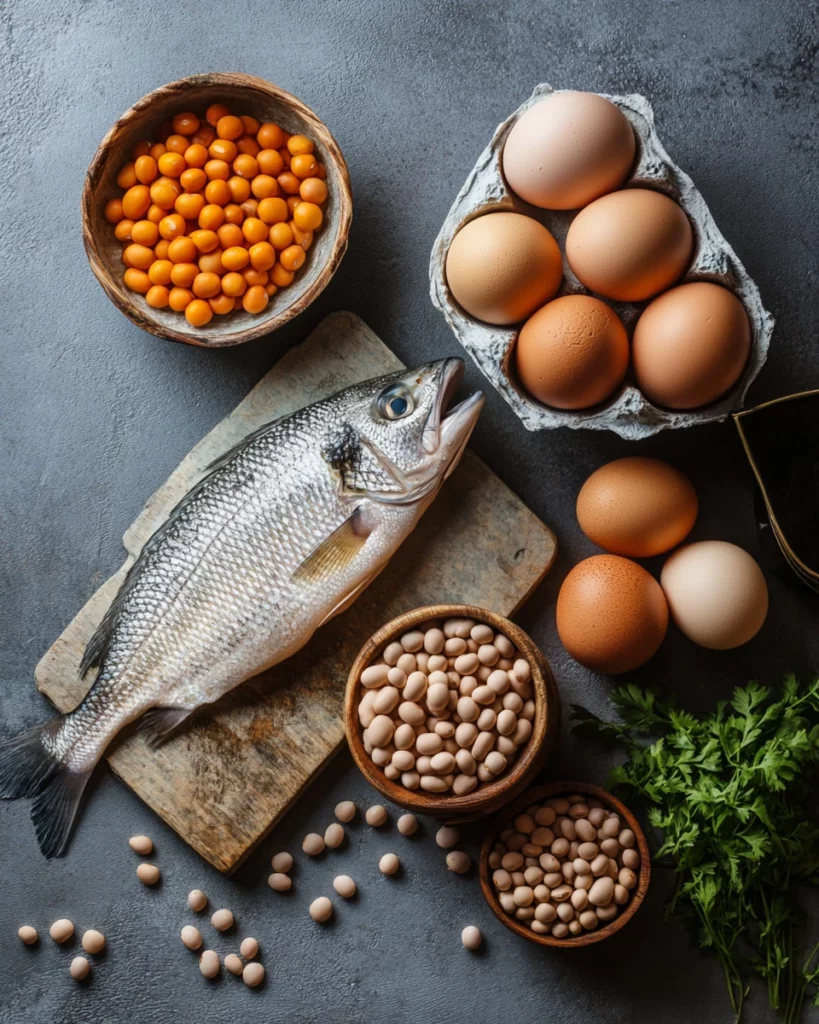
Food sources of choline
Choline is present in a variety of foods, but its levels vary depending on the source.
Foods such as eggs, meat, fish and legumes are the richest in choline.
Vegetarians and vegans may have difficulty getting enough choline, which can lead to choline deficiency.
It is important to include choline-containing foods in the diet, especially for people at increased risk of liver disease.
Recommendations for choline intake
Regular consumption of choline-rich foods is recommended to prevent liver disease and maintain overall health.
Adults should aim to consume 425-550 mg of choline per day, depending on age and gender.
It is important to consult a doctor about the need for supplementation if there is a risk of choline deficiency.
Conclusion
Choline is an important element in lipid metabolism and prevention of liver disease.
Its deficiency can lead to fat accumulation in the liver and the development of NAFLD and other diseases. Regular intake of choline through food or supplements can help maintain liver health and reduce the risk of disease.
Pay attention to your diet and try to include foods rich in this important nutrient.
List of references:
- Zhao, L., et al., “Choline Deficiency and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease,” Hepatology, 2019.
- Smith, S., et al., “Phosphatidylcholine and Fatty Liver Disease,” Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology, 2020.
- Yang, Y., et al., “Choline Intake and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Comprehensive Review,” Liver International, 2021.
- Hu, X., et al., “The Role of Choline in Liver Health and Disease,” Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 2022.
- Miller, M., et al., “Choline in Food Sources: A Critical Review,” Journal of Nutrition, 2019.
- West, A., et al., “Dietary Choline and Liver Health,” American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 2020.
- Choline Institute, “Choline: Dietary Sources and Recommendations,” 2020.
- Institute of Medicine, “Dietary Reference Intakes for Choline,” 2019.




