Scientific research confirms that collagen can support bone and joint health, reduce inflammation, and strengthen cartilage.
What is collagen and its role in the body?
Collagen is a protein that forms the basis of connective tissues such as cartilage, ligaments and bones.
There are more than 28 types of collagen in the human body, among which types I, II and III are the most important for joints.
- Type I is the basis for bones, tendons and skin.
- Type II – a key element of cartilage in joints.
- Type III – involved in the creation of elastic connective tissue.
How does collagen deficiency affect joints?
After the age of 30-40, natural collagen production begins to decline, leading to joint deterioration.
Recent studies have shown that decreased collagen levels are associated with the development of osteoarthritis and other joint diseases, manifested by pain, decreased mobility and inflammation.
Influence of lifestyle factors on collagen production:
- UV radiation
- Smoking
- Insufficient protein and vitamin C intake

Benefits of collagen for joints
Studies have shown that taking collagen can improve joint health in people with osteoarthritis, reducing inflammation and increasing mobility.
Specifically, collagen peptides are easily absorbed by the body, stimulating the body’s own collagen synthesis and slowing the breakdown of cartilage.
Key Benefits:
- Improved joint mobility – collagen strengthens cartilage and reduces inflammation.
- Injury prevention – supports healthy tendons and ligaments, which reduces the risk of injury.
- Injury rehabilitation – collagen helps speed recovery from fractures and surgery.

How do you incorporate collagen into your diet?
To maximize the benefits of collagen, it is important to include both supplements and foods that promote its production in the body in your diet.
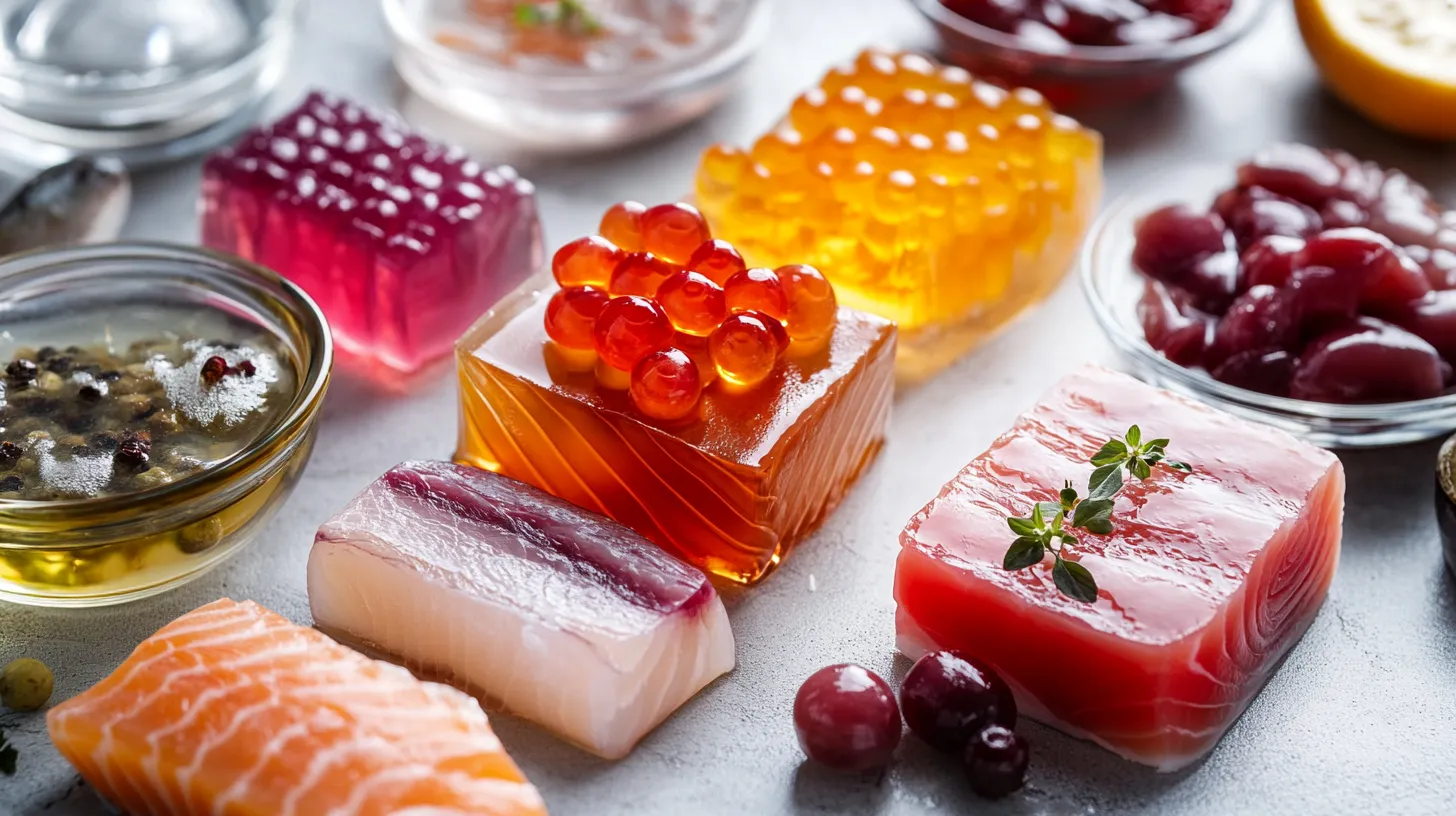

Products rich in collagen:
- Stews, cold cuts and bone broths
- Fish (especially salmon and tuna)
- Eggs, rich in amino acids
- Citrus fruits, broccoli and spinach for vitamin C

Recommendations for collagen intake:
- Powdered supplements: Collagen can be added to smoothies, tea or water. It is best to choose hydrolyzed collagen, which is easier to digest.
- Capsules: A convenient format for daily intake.
- Liquid forms: Drinkable forms of collagen, such as ProFlex, are more efficiently absorbed by the body through enzymatic processing.
Table of recommendations for collagen intake:
| Type of additive | Dosage | When to take |
|---|---|---|
| Collagen powder | 10 g per day | Mix with drinks |
| Collagen capsules | 1-2 capsules per day | With food or on an empty stomach |
| Liquid collagen | 15 ml per day | On an empty stomach for better absorption |
Current research
Research confirms that collagen peptides promote joint health, reduce osteoarthritis pain and speed recovery from injury.
- Animal studies show that collagen type II collagen type slow the destruction of cartilaginous tissue.
- Clinical trial among patients with osteoarthritis confirmed reduced pain sensation after 12 weeks of taking collagen supplements.
Conclusion
Collagen plays an important role in maintaining healthy joints and bones. Its regular consumption can significantly improve joint health, especially in older people or those suffering from joint disease.
However, it is important to remember that the effectiveness of collagen depends on lifestyle and the regularity of its intake.
It is recommended to consult a doctor before starting collagen supplements.
ProFlex – drinking collagen for joints
Collagen is poorly digested by the human body, because its molecules have a large size. Collagen is also poorly digested if a person suffers from various gastrointestinal diseases, as well as if we are talking about children or older people.
However, this process can be positively affected by using collagen peptides, i.e. short protein chains that include two or three amino acids. The size of their molecules is smaller, and therefore collagen peptides are digested much better.
Collagen is crushed by enzymatic hydrolysis, which allows to obtain peptides with low molecular weight and high content of basic amino acids – proline, glycine and hydroxyproline, which have high digestibility and are able to influence metabolic processes in cartilage.

These are the properties of the patented FORTIGEL collagen hydrolysate in the composition of ProFlex (ProFlex).
Taking drinking collagen for joints ProFlex (ProFlex) allows you to get deficient amino acids, on the basis of which the human body synthesizes its own collagen.
The advantages of ProFlex (ProFlex) are that it stimulates the synthesis of type II collagen, slows down the destruction of the collagen framework of cartilage, reduces pain and discomfort during increased physical activity and accelerates rehabilitation after surgical interventions.