
Perceptions of human health have radically changed since scientists began studying the gut microbiome.
Today, there is no doubt: the state of the microbiota affects not only digestion but also brain function, emotions, and mental health.
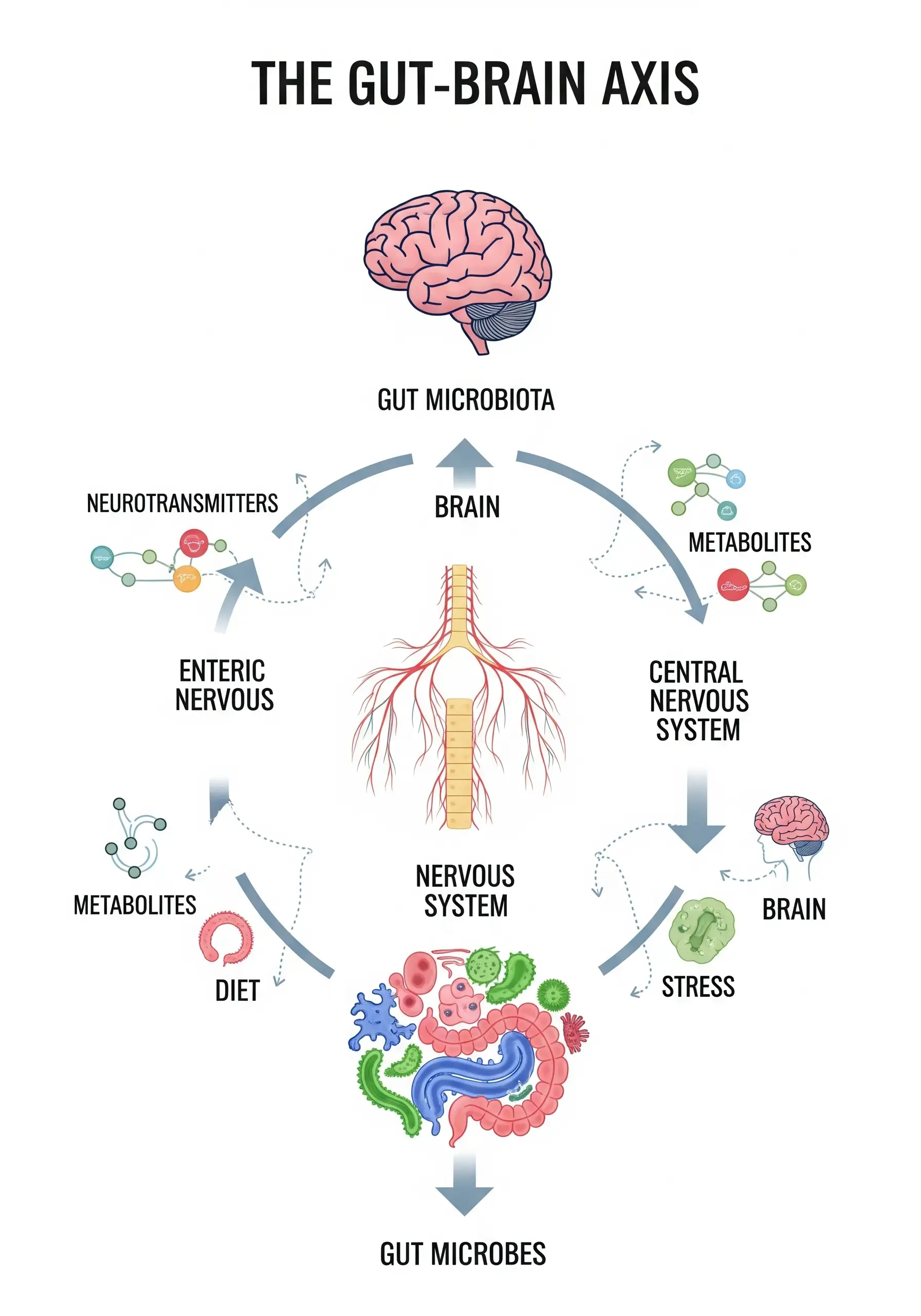
The term “gut–brain axis” describes the complex system of interactions between the nervous, immune, and endocrine systems, in which the microbiome plays a key role.
In 2025, the scientific community presented new discoveries confirming that microbiome modulation can be an effective tool for preventing and treating anxiety, depression, and cognitive disorders.

How does the gut affect the brain?
The microbiome and the brain communicate through several pathways:
-
Neurotransmitters. Bacteria synthesize serotonin, GABA, and dopamine. For example, Lactobacillus can influence GABA levels, reducing anxiety.
-
Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). Products of fiber fermentation (butyrate, propionate) affect inflammation and neuroplasticity.
-
Immune system. Microbiota imbalance increases gut permeability and pro-inflammatory cytokines, which is associated with depression.
-
Vagus nerve. The main “communication pathway” between the gut and the brain.

New discoveries in 2025
At the Vitafoods Europe and SupplySide West 2025 exhibitions, several key studies were presented:
-
Postbiotics against stress. Bacterial metabolites (e.g., peptides and SCFAs) have shown effectiveness in reducing anxiety symptoms in clinical trials.
-
Personalized probiotics. Microbiome genetic analysis allows selection of strains for specific psycho-emotional states (e.g., Bifidobacterium longum for anxiety, Lactobacillus helveticus for depression).
-
Next-generation symbiotics. Combining probiotics with prebiotic fibers and polyphenols provides a stronger effect in maintaining mood stability.
Table 1. Role of the microbiome in mental health
| Mechanism | Example | Potential effect |
|---|---|---|
| Neurotransmitter production | Lactobacillus → GABA, serotonin | Reduced anxiety |
| SCFAs (butyrate, propionate) | Fiber fermentation | Anti-inflammatory effect, improved cognitive function |
| Immune regulation | Reduced cytokine levels | Fewer depressive symptoms |
| Communication via vagus nerve | Signals from microbes | Mood balance, stress resilience |

Practical approaches in 2025
Microbiome modulation for mental health support includes several strategies:
-
Probiotics. Most studied are Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Bifidobacterium longum, L. helveticus.
-
Prebiotics. Dietary fibers (inulin, fructooligosaccharides) nourish “beneficial” microbes.
-
Postbiotics. Bacterial metabolites with proven effects on the nervous system.
-
Diet. A Mediterranean diet high in vegetables, fruits, nuts, and omega-3 is associated with a lower risk of depression.
Table 2. Practical applications in different situations
| Situation | Recommended solution | Additional advice |
|---|---|---|
| Chronic stress | Probiotics (L. helveticus, B. longum) | Breathing exercises, yoga |
| Sleep disturbances | Postbiotics + magnesium | Sleep routine, limiting gadgets |
| Depressive symptoms | Symbiotics with fibers and polyphenols | Mediterranean diet |
| Students during exams | Probiotics + omega-3 | Balance study and rest |
| People 50+ | Personalized probiotics | Monitoring inflammatory markers |

FAQ — frequently asked questions
1. Can probiotics replace antidepressants?
No. They may be an adjunctive tool, but do not replace pharmacotherapy.
2. Which foods are best for the microbiome in autumn?
Fermented vegetables, yogurts, kefir, fiber from fruits and legumes.
3. How long does it take to see effects from probiotics?
Usually, initial changes are noticeable after 4–6 weeks of regular intake.
Conclusion
The microbiome represents a new dimension in mental health medicine.
2025 research confirms: maintaining a proper microbial balance can influence anxiety levels, mood, and even cognitive function.
For clinicians, this means additional tools, and for patients, a simple way to support mental health through nutrition and nutraceuticals.
References
-
O’Toole PW, Jeffery IB. Gut microbiota and aging. Science. 2025.
-
Steenbergen L. et al. A randomized controlled trial of multispecies probiotics in reducing stress in healthy volunteers. Brain Behav Immun. 2020.
-
Dinan TG, Cryan JF. Gut microbiota: a new therapeutic target in mental illness. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017.
-
Hao Q. et al. Probiotics for preventing anxiety and depression: a systematic review. Nutrients. 2022.
-
EFSA. Scientific opinion on health benefits of probiotics and postbiotics. EFSA Journal. 2024.




