
Why does the immune system need help?
The immune system is a complex network of cells and molecules tasked with protecting the body from viruses, bacteria and other external threats.
But stress, age, chronic illness, sleep and nutrient deficiencies weaken immune defenses.
Therefore, key nutrients such as vitamin C and zinc become essential in supporting immune resilience, especially during periods of infectious risk.
Vitamin C: antioxidant and protector
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) is a water-soluble antioxidant that:
-
activates phagocytosis – capture of pathogens by immune cells,
-
stimulates interferon production,
-
promotes regeneration of epithelial barriers.
Vitamin C has been found to reduce the duration of colds by about 8% in adults and up to 14% in children when taken regularly【1】.
It also affects collagen production, which is particularly important for the integrity of the skin barrier, the first line of immune defense, especially relevant in dermatology.

Zinc: conductor of the immune orchestra
Zinc is a trace element involved in over 300 enzymatic reactions, including:
-
in the development and activation of T-lymphocytes,
-
stabilization of cell membranes,
-
in tissue healing.
In zinc deficiency, there is an increased susceptibility to infections, especially viral【2】. Zinc can also inhibit the replication of viruses in vitro, including rhinoviruses and coronaviruses.

Combination of vitamin C and zinc: synergy of action
The combined use of vitamin C and zinc has a synergistic effect:
-
reducing the severity and duration of colds,
-
reducing the frequency of recurrences in immunodeficient patients,
-
support in acute respiratory viral infections.
Studies show that the combination of these nutrients can shorten the duration of cold symptoms by 1-2 days with adequate dosage【3】.
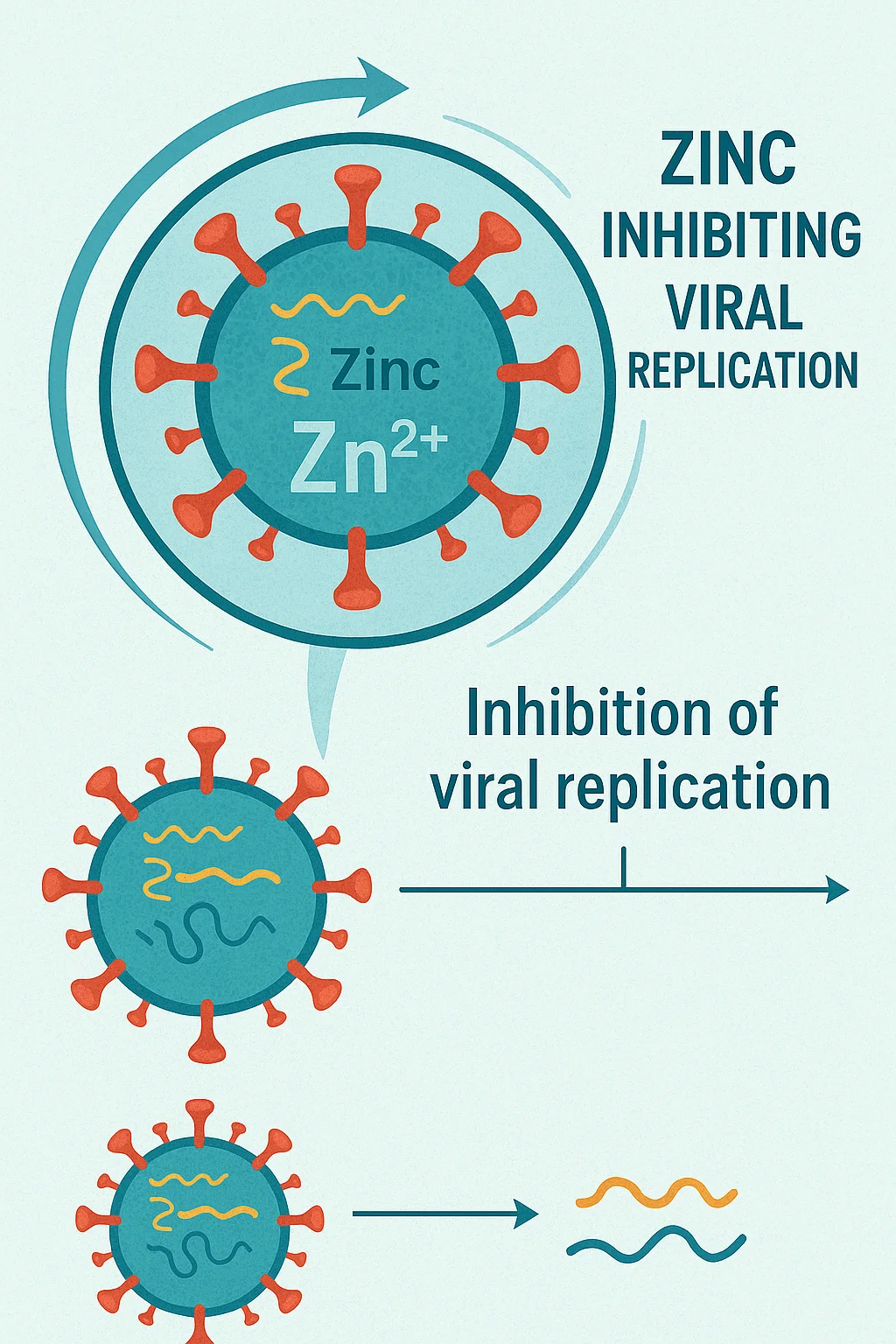
Who is especially important to receive?
Supplemental intake of vitamin C and zinc is recommended:
-
elderly people;
-
people with chronic diseases;
-
when there’s a high incidence of viral illnesses;
-
during seasonal epidemics;
-
stress and intense exertion;
-
smokers and residents of polluted regions.
Trends 2025: what’s on show at Vitafoods
Vitafoods Europe 2025 showcases new delivery systems that improve the bioavailability of zinc and vitamin C:
-
Liposomal forms – for better absorption;
-
Fizzy tablets and chewable lozenges – convenient for people who have trouble swallowing;
-
Gummies – particularly popular with young adults and the elderly.
There has also been an emphasis on sustained-release forms, which reduce the risk of gastric irritation from zinc and allow for more stable blood levels.
Why are these two nutrients often included in immune support formulas?
It’s not only because of their prominence, but also because of their well-studied mechanisms of action.
Below is a brief overview of the key functions of vitamin C and zinc that make them important components of preventing and restoring the immune response:
Table 1. Functions of vitamin C and zinc in the immune system
| Nutrient | Main effects |
|---|---|
| Vitamin C | Antioxidant, enhance phagocytosis, barrier support |
| Zinc | T-cell modulation, antiviral activity, healing |
Table 2. Forms and dosages in dietary supplements (average values)
| Formulation | Vitamin C (mg) | Zinc (mg) | Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fizzy tablets | 500–1000 | 10 | Quick release |
| Gummy | 100–250 | 5–10 | Convenience of intake, high compliance |
| Prolonged-release tablets | 250–500 | 10–15 | Gradual release |
| Liposomal forms | 250–1000 | 10–20 | Increased bioavailability |
Conclusion and recommendations
Vitamin C and zinc is a classic, scientifically proven combination to support immune function.Modern delivery systems make the intake of these nutrients more convenient and effective. Regular consumption in physiologic dosages is safe and recommended in case of increased immune stress.
List of references
-
Hemilä H. Vitamin C and infections. Nutrients. 2017;9(4):339.
-
Prasad AS. Zinc in human health: effect of zinc on immune cells. Mol Med. 2008;14(5-6):353–357.
-
Ran L, Zhao W, Wang J, Wang H, Zhao Y, Tseng Y. Extra dose of vitamin C based on a population survey: efficacy against the common cold. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(2): 884–892.



