Tonsillitis is an inflammation of the palatine tonsils, which can bring significant discomfort and lead to serious complications in the absence of timely treatment.
In this article we will consider in detail what provokes tonsillitis, how to properly diagnose and treat it, as well as interesting facts about tonsils.

Causes of tonsillitis
The main cause of tonsillitis is infection of the tonsils by bacteria or viruses.
The most common causative agents are:
- Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus is the most common bacterial cause.
- Adenoviruses, rhinoviruses, and influenza vir uses are common viral agents.
Risk factors that contribute to the development of tonsillitis:
- Excessive cold.
- Reduced immunity.
- Chronic diseases of the nasopharynx.
- Contact with infected people.
Symptoms and signs of tonsillitis
Tonsillitis can manifest acutely or take a chronic form.
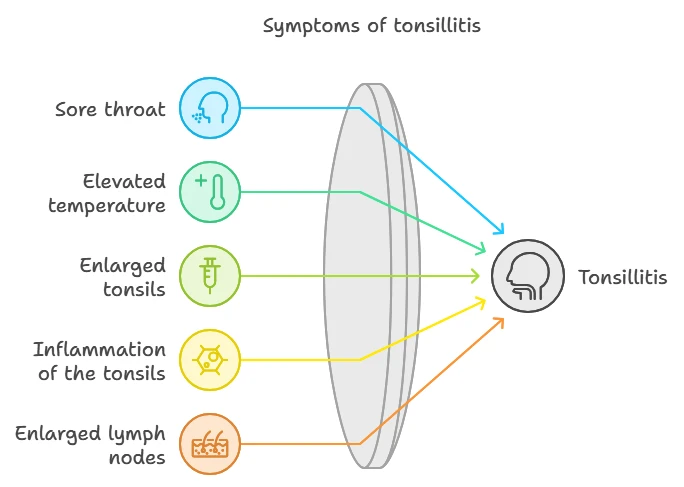
Main symptoms:
- A sore throat that gets worse when swallowing.
- Increased body temperature.
- Enlargement and redness of the tonsils.
- Plaque or purulent plugs on the tonsils.
- Enlargement of cervical lymph nodes.
Table 1. Comparison of acute and chronic forms of tonsillitis
| Symptom | Acute tonsillitis | Chronic tonsillitis |
|---|---|---|
| Sore throat | Expressed | Moderate |
| Temperature | High | Normally normal |
| General well-being | Sharp deterioration | Satisfactory |
| Recurrence rate | Rarely | Often |

Tonsillitis in children: features and frequency
Tonsillitis is most common in children between the ages of 5 and 15.
In children, the immune system is not yet fully formed, which makes them more vulnerable to infections.
Features of tonsillitis in children:
- Rapid development of symptoms.
- More pronounced intoxication.
- Possibility of developing complications such as rheumatism.

Diagnosis of tonsillitis: the correct algorithm
For an accurate diagnosis of tonsillitis it is necessary to consult an otorhinolaryngologist.
The diagnostic algorithm includes:
- Collection of anamnesis and complaints of the patient.
- Physical examination: examination of the throat, palpation of lymph nodes.
- General bloodLaboratory tests.
- throat swab to determine the causative agent and its sensitivity to antibiotics.
Effective treatments for tonsillitis
Treatment of tonsillitis depends on its form and severity.
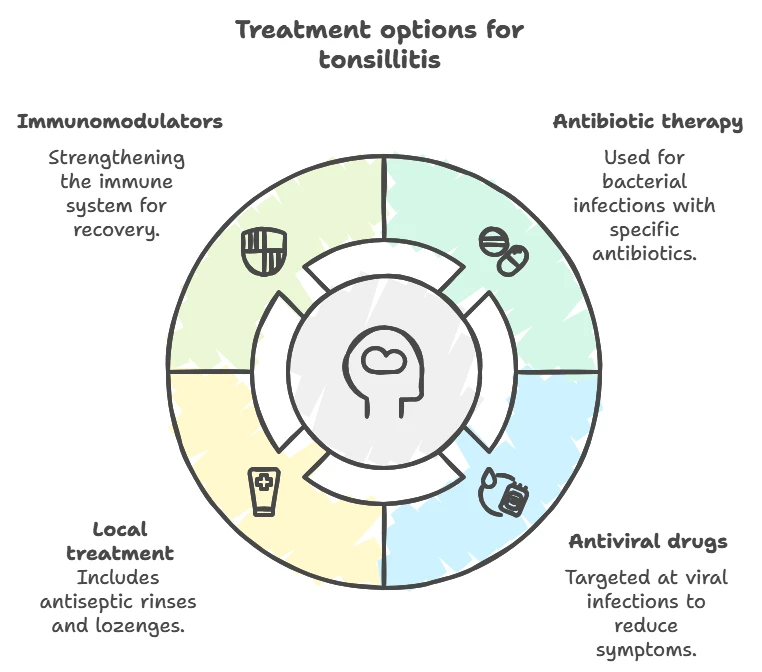
Conservative treatment
- Antibiotic therapy (for bacterial infection): penicillins, cephalosporins.
- Antiviral drugs (for viral etiology).
- Local treatment: rinses with antiseptics, lozenges.
- Immunomodulators to strengthen immunity.
Surgical treatment of tonsillitis: when is it necessary to remove tonsils?
Tonsillectomy, or removal of the tonsils, may be necessary under certain conditions.
This surgical method is used when conservative treatment fails or when chronic tonsillitis causes serious discomfort and increases the risk of complications.
Indications for tonsillectomy
1. Chronic tonsillitis with frequent exacerbations.
Tonsillectomy is indicated if the patient suffers from frequent sore throats that occur more than 5 times a year.
Such frequent relapses significantly affect the quality of life of a person, reducing the ability to work and worsening general well-being.
Constant exacerbations lead to chronic fatigue, decreased immunity and other unpleasant consequences.
2 Lack of effect from conservative treatment.
If the use of antibiotics, antiseptic rinses, physiotherapy and other methods of conservative treatment does not give positive results, the doctor may recommend surgical intervention.
In such cases, tonsils become a chronic source of infection and lose their protective function, which makes them useless and even harmful to the body.
3 Complications of chronic tonsillitis.
Possible complications for which tonsil removal is recommended include paratonsillar abscess, rheumatism, glomerulonephritis and other diseases caused by the spread of infection.
Paratonsillar abscess, for example, is a purulent inflammation that may require emergency surgery.
4. obstructive sleep apnea.
The tonsils, enlarged due to chronic inflammation, can block the airway, causing obstructive sleep apnea.
This condition is characterized by breathing stops during sleep, leading to poor sleep quality and increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Tonsillectomy in this case helps to restore normal breathing.

Benefits and risks of tonsillectomy
Removal of tonsils can reduce the frequency of throat infections and improve the patient’s quality of life.
After tonsillectomy, most patients report a significant improvement in their condition, less sore throat and a decreased risk of complications.
However, like any surgical procedure, tonsillectomy has its risks. The main ones include:
- Bleeding: bleeding may occur after surgery and requires medical supervision.
- Pain: in the first few days after surgery, the patient may experience a sore throat that requires pain medication.
- Infections: although the risk of infection after tonsillectomy is low, it still exists.
It is important to note that the decision to perform a tonsillectomy is made by the doctor based on the clinical picture and the patient’s condition.
The physician considers all the risks and benefits of the procedure to provide the most effective treatment for each individual patient.
Table 3: Benefits and risks of tonsillectomy
| Advantages | Risks |
|---|---|
| Reducing the incidence of throat infections | Bleeding after surgery |
| Reducing pain and inflammation | Sore throat in the postoperative period |
| Prevention of complications (rheumatism) | Risk of infection |

Tonsillectomy can significantly improve the patient’s quality of life, especially in the presence of frequent exacerbations and lack of effect of conservative treatment.
Consultation with an otorhinolaryngologist and a thorough examination will help to make the right decision about the need for this operation.
Interesting facts about tonsils
- The name “ tonsils” comes from the Latin word tonsillae, meaning “almond”, because of the similarity in shape.
- The tonsils are the body’s first line of defense against infections that enter through the mouth and nose.
- According to research, the tonsils are involved in building immunity in early childhood.

Prevention of tonsillitis
- Personal hygiene: regular hand washing.
- Strengthening immunity: balanced diet, vitamins.
- Avoiding hypothermia and contact with sick people.
Conclusion
Tonsillitis is a serious disease that requires timely diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding the causes and signs of tonsillitis will help prevent complications and preserve your health.
Seek professional help at the first sign of symptoms and follow the recommendations for prevention.
Studies show that seeking medical attention early and following your doctor’s advice significantly improves the effectiveness of tonsillitis treatment.