
In today’s society, many people face chronic fatigue and decreased energy levels.
Constant stress, busy schedules and lack of attention to nutrition can lead to feelings of exhaustion and decreased productivity.
Nutrition plays a key role in maintaining the body’s energy levels and overall well-being.
The right diet can not only increase energy but also improve overall health.

The physiology of energy
The body gets energy from the food we eat. This energy is needed to perform vital functions: breathing, heartbeat, brain function and physical activity.
The main sources of energy are macronutrients:
- Carbohydrates: the main source of energy, especially for the brain and muscles.
- Protein: serves as a building material and can be used as a source of energy when carbohydrates are scarce.
- Fats: a concentrated source of energy necessary for the absorption of some vitamins.
Micronutrients, such as vitamins and minerals, do not provide energy directly, but play an important role in metabolic processes by helping to convert food into energy.
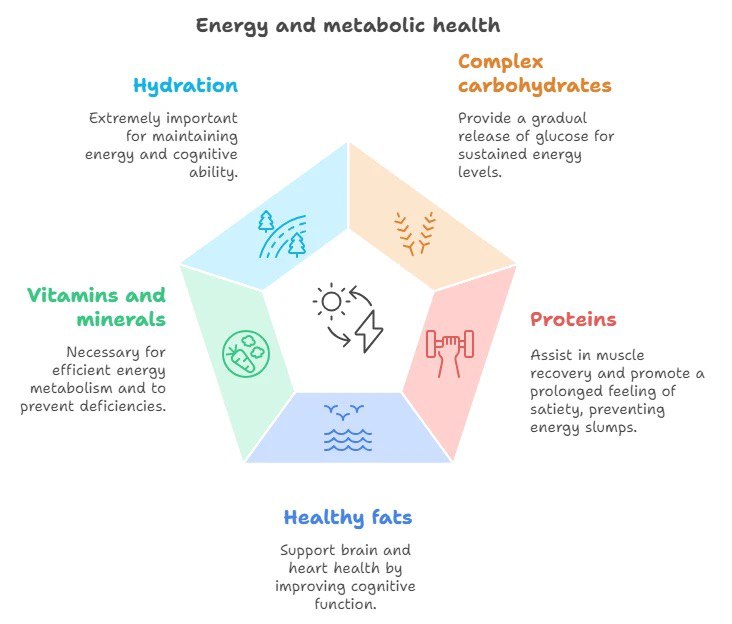
Foods that promote energy conservation
Complex carbohydrates
-
- Whole Grains: whole grain breads, pastas and cereals contain more fiber and nutrients than refined grains, providing a steady flow of energy.
- Oatmeal: rich in fiber and slowly digestible carbohydrates, which helps maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- Brown rice: contains B vitamins and magnesium, essential for energy metabolism.

Protein
- Lean meats: chicken, turkey are excellent sources of protein with low saturated fat content.
- Fish: salmon, tuna, mackerel are rich in omega-3 fatty acids.
- Legumes: beans, lentils, chickpeas are rich in vegetable protein and fiber.

Healthy fats
- Avocado: contains monounsaturated fats and potassium.
- Nuts and seeds: almonds, walnuts, chia seeds are sources of healthy fats and magnesium.
- Olive oil: rich in antioxidants and monounsaturated fats.

Vitamins and minerals
- Iron: spinach, red meat, legumes are essential for the formation of hemoglobin, which transports oxygen to cells.
- Magnesium: nuts, seeds, whole grains are involved in more than 300 enzymatic reactions, including energy production.
- B vitamins: eggs, dairy products, whole grains are important for the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins and fats.
Hydration
- Water: essential for all body processes, including nutrient transportation and waste elimination.
- Herbal teas: can help hydrate and provide additional nutrients.

Mechanisms of action
The body’s energy balance depends on many factors, among which nutrition plays one of the key roles.
Properly selected foods not only provide us with the necessary calories, but also influence the speed and efficiency of metabolic processes.

Understanding how different nutrients affect energy levels helps you make informed choices about foods that promote alertness and performance.
- Complex carbohydrates provide a gradual release of glucose into the bloodstream, keeping energy levels stable without sudden peaks and troughs. Studies show that consuming whole grain products is associated with increased energy levels and improved metabolic health.
- Protein helps with muscle and tissue repair and promotes a prolonged feeling of satiety, which prevents overeating and energy slumps.
- Healthy fats, especially omega-3 fatty acids, support brain and cardiovascular health, improving cognitive function and mood.
- Vitamins and minerals are essential for efficient energy metabolism. For example, iron deficiency can lead to anemia and chronic fatigue.
- Hydration is vital, as dehydration of even 1-2% can significantly reduce energy levels and cognitive ability.
Table 1. Key foods for sustaining energy
| Category | Examples of products | Energy benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Complex carbohydrates | Oatmeal, whole wheat bread, brown rice | Stable blood sugar levels |
| Protein | Chicken, fish, legumes | Восстановление и поддержание мышечной массы |
| Healthy fats | Avocado, nuts, olive oil | Поддержка здоровья мозга и сердца |
| Vitamins and minerals | Spinach, eggs, dairy products | Участие в метаболических процессах |
| Hydration | Water, herbal teas | Optimization of body functions |

Practical recommendations
- Start the day with a nutritious breakfast: oatmeal with berries and nuts will give you energy for the morning.
- Include protein at every meal: add chicken or legumes to salads and main courses.
- Use healthy fats: dress salads with olive oil or add avocado to sandwiches.
- Keep hydrated: carry a bottle of water and drink regularly throughout the day.
- Plan snacks: nuts, yogurt or fruit can help maintain energy levels between meals.
- Limitations and contraindications: if you have allergies or chronic diseases, consult your doctor or nutritionist before changing your diet.
Table 2. Approximate menu for a day
| Meal | Dish | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Breakfast | Oatmeal with berries and almonds | Rich in fiber and healthy fats |
| Snack | An apple and a handful of nuts | Provides a quick energy boost |
| Lunch | Salad with quinoa, spinach, chicken and avocado | A combination of protein, carbohydrates and healthy fats |
| Snack | Greek yogurt with honey | Source of protein and probiotics |
| Dinner | Baked fish with brown rice and steamed vegetables | Provides omega-3 fatty acids and complex carbohydrates |
Conclusions
Proper nutrition is the foundation for maintaining high energy levels and overall well-being.
Including a variety of foods rich in essential nutrients in your diet can help you fight fatigue and improve your quality of life.
Pay attention to your diet and make healthy food choices to feel energized every day.
Note: It is recommended that you consult a nutritionist or doctor before making major dietary changes.



