Genetic testing and personalized medicine are becoming increasingly popular trends in medicine.
These technologies allow physicians to select the most appropriate treatments based on a patient’s individual genetic characteristics, which significantly increases the effectiveness of therapy.
In this article, we will discuss recent advances in genetic testing, review their role in personalized medicine, and provide examples of successful research in this area.

What is genetic testing?
Genetic testing is the analysis of DNA to detect mutations, disease predispositions, or individual drug metabolism.
This method helps to detect genetic changes that may affect the development of diseases or the body’s response to certain treatments.
An example is testing for BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutations to determine the risk of developing breast or ovarian cancer.
According to a study conducted by the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), early detection of mutations in these genes contributes to a significant reduction in mortality through preventive measures and more accurate monitoring (ASCO, 2023).

Personalized medicine: a new word in treatment
Personalized medicine uses genetic testing to develop individualized approaches to patient care.
This is particularly important in the treatment of cancer, where a “one size fits all” approach is no longer always effective.
By analyzing the genetic profile of the tumor, the most appropriate drugs can be selected and thus increase the chances of successful treatment.
Table 1. Benefits of personalized medicine
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased effectiveness of treatment | Treatment is individualized, which increases its effectiveness. |
| Reduced side effects | Reducing unnecessary medications and dosages, which reduces the likelihood of complications. |
| Disease prevention | Ability to predict and prevent the development of certain diseases. |

Real studies and their results
Recent studies show that the use of genetic testing in oncology can improve overall patient survival. In a study conducted in 2022 by the US National Cancer Institute, it was found that patients with a mutation in the EGFR gene who received targeted therapy lived an average of 30% longer than patients who received standard treatment (NIH, 2022).
Genetic testing has also found application in the field of cardiology. For example, testing for the presence of LDLR gene mutations can identify predisposition to hypercholesterolemia and thus enable measures to be taken to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Table 2. Applications of genetic testing in different fields of medicine
| Medical field | Examples of genetic testing | Purpose of testing |
| Oncology | BRCA1/BRCA2, EGFR | Risk identification and therapy selection |
| Cardiology | LDLR, APOE | Prevention of cardiovascular diseases |
| Psychiatry | Sequencing of serotonin receptor-related genes | Drug selection for depression and anxiety disorders |
Issues and challenges
Despite the obvious advantages, genetic testing also has its limitations.
These include the high cost of the tests, the need for qualified specialists to interpret the results, and ethical considerations.
For example, information about predisposition to serious diseases may cause anxiety in the patient and lead to undesirable consequences if proper psychological support is not provided.
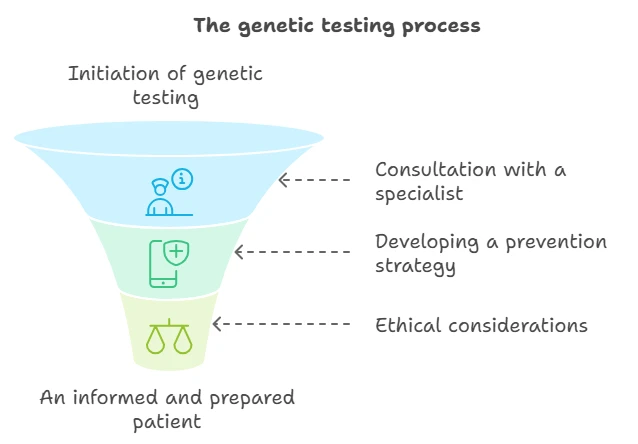
Recommendations
- Consultation with specialists. Before undergoing genetic testing, you should consult with a geneticist who can properly explain the results and suggest next steps.
- Prevention based on the results. Using genetic testing data to develop an individualized disease prevention program can significantly improve quality of life.
- Ethical awareness. It is important to consider the ethical and psychological aspects of genetic testing. Patients should be prepared for the possible results and have access to qualified psychological support.
Conclusion
Breakthroughs in genetic testing and personalized medicine are opening up new opportunities for the treatment and prevention of diseases.
An individualized approach to each patient can increase the effectiveness of therapy, reduce the risk of side effects and significantly improve quality of life.
However, to realize the full potential of these technologies, ethical considerations must be taken into account and genetic testing must be made available to all those who need it.
Sources
- American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO). “BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutation Testing.” ASCO, 2023. https://www.asco.org
- National Institutes of Health (NIH). “EGFR Mutation and Targeted Therapy Outcomes.” NIH, 2022. https://www.nih.gov