Autumn is the time when our immune system especially needs support.
Returning to work and school, less sunlight, and temperature fluctuations — all of these increase the risk of colds and reduce the body’s natural resistance.
Among the nutrients most often recommended by doctors in autumn are vitamin D, zinc, and probiotics. Their synergy creates a strong foundation for protection against infections and supports gut health — a key component of the immune system.
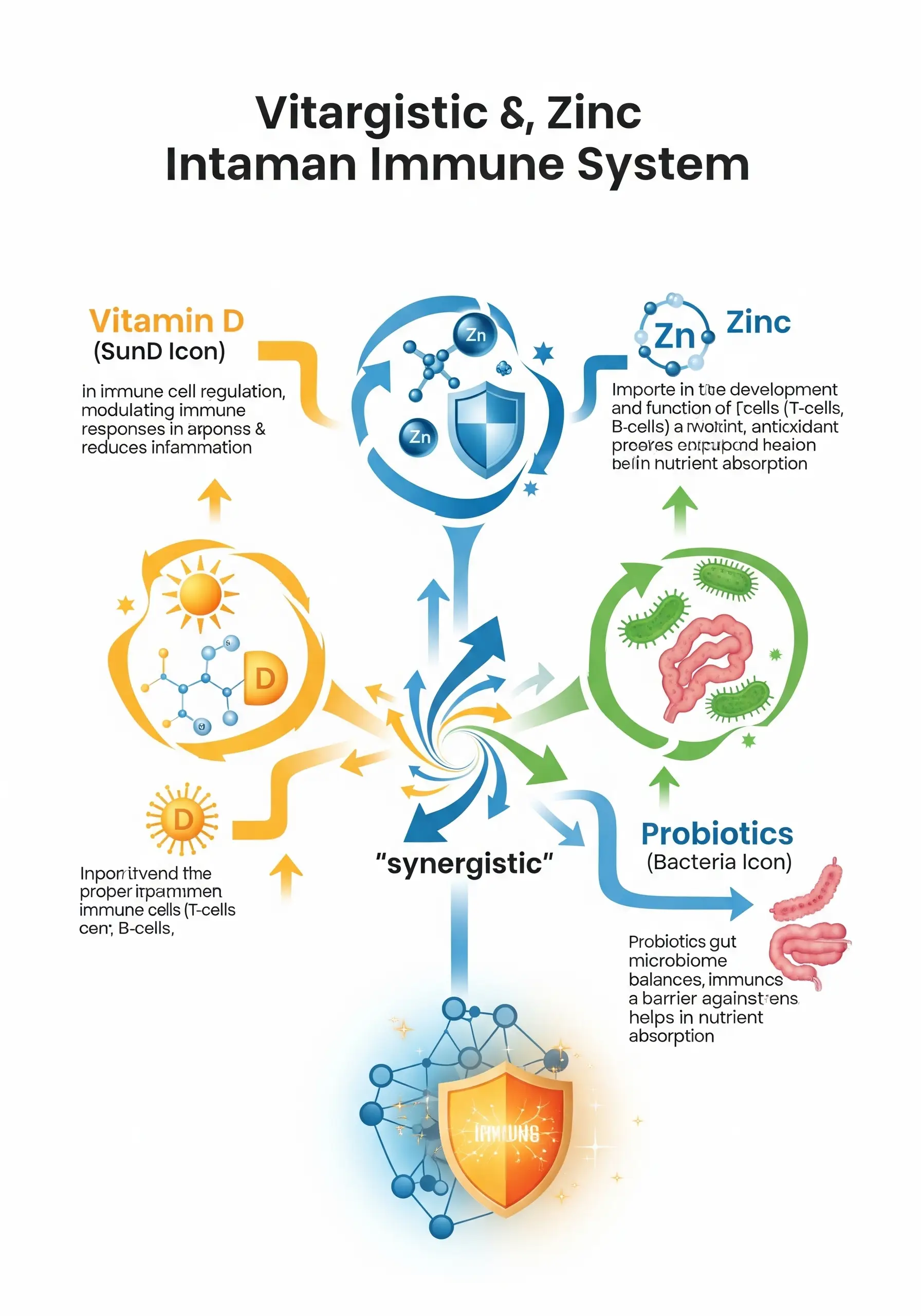
Vitamin D: the “sunshine” vitamin
Vitamin D regulates over 200 genes and affects T-lymphocyte activation. Its deficiency in autumn in Ukraine is widespread due to reduced sun exposure.
-
Research Martineau et al., 2017 showed that regular vitamin D intake reduces the risk of respiratory infections by 12%.
-
Sources: sun (in summer), fatty fish, fortified foods, and supplements.
Zinc: mineral for immune cells
Zinc participates in over 300 enzymes and is critical for lymphocyte differentiation.
-
Its deficiency is associated with more frequent infections, delayed wound healing, and reduced sense of smell.
-
A meta-analysis Rao et al., 2011 showed that zinc intake at the first symptoms of a cold shortens illness duration by 1–2 days.

Probiotics: gut microbiome balance
About 70% of immune system cells are located in the gut. Probiotics are live microorganisms that restore microbiota balance and strengthen barrier functions.
-
In a study Hao et al., 2015 in children and adults, probiotics reduced the risk of upper respiratory tract infections by 47%.
-
Most studied strains: Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, Bifidobacterium lactis.
Table 1. Key nutrients for immunity in autumn
| Nutrient | Main Action | Sources | Average Daily Dose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin D | T-cell activation, anti-inflammatory effect | Fish, eggs, supplements | 1000–2000 IU |
| Zinc | Lymphocyte differentiation, antiviral activity | Meat, pumpkin seeds, supplements | 10–15 mg |
| Probiotics | Microbiome balance, gut barrier support | Fermented foods, capsules, powders | 10⁹–10¹¹ CFU/day |

Practical application: combined approaches
In autumn, it is important not only to know which nutrients to take but also in what combination.
Today, manufacturers offer complex formulas — vitamin D combined with zinc and probiotics.
This approach works on three levels: immune cells, antioxidant protection, and microbiome health.
Table 2. Practical application of nutrients in autumn
| Situation | Recommended Nutrients | Additional Advice |
|---|---|---|
| Frequent colds | Vitamin D + Zinc | Check blood vitamin D levels |
| Weakened gut | Probiotics | Add prebiotic fibers |
| Office work | Vitamin D, Probiotics | Take breaks in fresh air |
| School-age children | Probiotics + Zinc | Monitor diet |
| People 50+ | Vitamin D + Zinc + Probiotics | Regular microbiome check |
FAQ — common questions
1. Can I take vitamin D without a blood test?
A short course at a preventive dose (1000 IU) in autumn is safe, but for long-term intake, it is better to test 25(OH)D levels.
2. Should zinc be combined with other minerals?
Yes, but avoid taking it simultaneously with high doses of iron, as they reduce each other’s absorption.
3. Which probiotics are best in autumn?
The most studied combinations are Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. Pay attention to CFU count and specific strains.
Conclusion
Autumn is the period when our immune system especially needs support. Vitamin D, zinc, and probiotics act synergistically, strengthening the body’s defenses.
Their regular intake helps reduce the risk of colds, maintain a healthy microbiome, and stay active even during the high-demand season.
References
-
Martineau AR. et al. Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory infections: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2017.
-
Rao S. et al. Zinc supplementation for preventing respiratory tract infections. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011.
-
Hao Q, Dong BR, Wu T. Probiotics for preventing acute upper respiratory tract infections. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015.
-
EFSA. Scientific opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to vitamin D. EFSA Journal. 2016.
-
Calder PC. Nutrition, immunity and COVID-19. BMJ Nutrition, Prevention & Health. 2020.