Antibiotics were one of the greatest medical discoveries of the 20th century. They made it possible to effectively fight previously deadly infections, saving millions of lives around the world.
However, today mankind faces a serious challenge – growing antibiotic resistance.
In Ukraine, this problem is of particular relevance due to a combination of medical, social and economic factors.
Understanding the causes and consequences of this phenomenon is extremely important for each of us.
What is antibiotic resistance?
Antibiotic resistance is the ability of bacteria to change so that they become immune to the effects of antibiotics.
This occurs due to natural genetic mutations or the acquisition of resistance genes from other bacteria.
As a result, drugs that were previously effective no longer work, making infections more difficult to treat.
How does resistance develop?
- Natural selection: When antibiotics are used, they kill sensitive bacteria but may leave alive those that have mutations that allow them to survive.
- Horizontal gene transfer: Bacteria can exchange genes, including those that confer resistance, through the processes of conjugation, transformation and transduction.
- Overuse and misuse of antibiotics: Frequent and inappropriate use of antibiotics increases the pressure on bacteria, accelerating the development of resistant strains.

Situation in Ukraine
Ukraine faces serious public health challenges, and antibiotic resistance is one of the most acute.
According to the Ministry of Health of Ukraine, there has been a significant increase in resistant infections in recent years, especially in hospitals and health care facilities.
Factors affecting the situation:
- Inadequate monitoring of antibiotic sales: Despite legal restrictions, many pharmacies continue to sell antibiotics without prescriptions.
- Lack of national monitoring programs: Insufficient tracking and reporting of resistance cases makes it difficult to understand the scale of the problem.
- Socio-economic constraints : Low public awareness and limited access to quality health care exacerbate the situation.
Table 1. Level of resistance of some bacteria to antibiotics in Ukraine
| Bacterium | Antibiotic | Resistance level (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Staphylococcus aureus | Methicillin (MRSA) | 45% |
| Escherichia coli | Fluoroquinolones | 35% |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | Carbapenems | 25% |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Cephalosporins | 30% |
| Acinetobacter baumannii | Multidrug resistance | 50% |
Source: Ministry of Health of Ukraine, 2021.
Causes of increasing antibiotic resistance
Self-medication and uncontrolled use of antibiotics
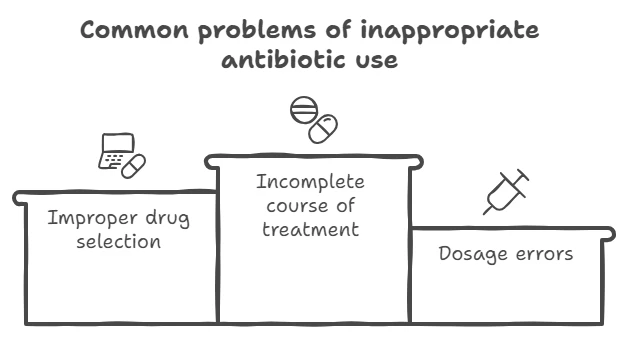
Many Ukrainians, at the first signs of a cold or malaise, self-prescribe antibiotics, considering them a panacea. This leads to several problems:
- Wrong choice of drug: Antibiotics are not effective against viral infections, but they are often taken for flu or acute respiratory infections.
- Incomplete treatment: Patients may stop taking antibiotics at the first sign of improvement, which does not completely kill the bacteria.
- Overdose or insufficient dosage : Failure to follow recommended dosages may contribute to the development of resistance.
Selling antibiotics without a prescription
Despite existing laws regulating the sale of antibiotics, the reality is that many pharmacies continue to dispense them without a doctor’s prescription. This facilitates access to the drugs and contributes to their misuse.

Use of antibiotics in agriculture
Antibiotics are widely used in animal husbandry to prevent disease and promote animal growth. This leads to the emergence of resistant bacteria that can be transmitted to humans through food products.
Lack of awareness
The lack of educational campaigns and insufficient media attention to the problem leads to the population not realizing the seriousness of the situation and not knowing about the proper use of antibiotics.

Non-compliance with infection control in health care facilities
Lack of adherence to hygiene standards and protocols in hospitals contributes to the spread of resistant strains among patients.

Public health implications
Increased incidence of severe and intractable infections
Resistant bacteria cause infections that require longer and more complex treatment. This can lead to a worse prognosis and an increased risk of complications.
Increase in mortality
The lack of effective antibiotics means that common infections can become fatal. WHO estimates that by 2050, the number of deaths from resistant infections could exceed cancer deaths.
Economic costs
Treatment of resistant infections requires the use of more expensive drugs and additional medical services. This increases the financial burden on both the health care system and patients.
Table 2: Economic consequences of antibiotic resistance in Ukraine
| Indicator | Significance |
|---|---|
| Additional treatment costs | $150 million annually |
| Increased length of hospitalization | +10 days on average |
| GDP losses due to lower labor productivity | $500 million annually |
| Cost of developing new antibiotics | Over $1 billion for the drug |
Source: Economic Review of the Ministry of Health of Ukraine, 2021.
Social consequences
- Decreased quality of life: Chronic infections and prolonged treatment have a negative impact on the physical and emotional well-being of patients.
- Deterioration of public health: The spread of resistant bacteria can lead to epidemics and worsen the epidemiological situation in the country.

How to prevent further development of the problem
Compliance with doctor’s recommendations
- Take antibiotics only as prescribed: It is important to use antibiotics only when they are really needed and prescribed by a qualified specialist.
- Complete the full course of treatment: Even if symptoms have improved, it is important to complete the course to completely eliminate the infection.
- Do not use leftover antibiotics: Do not keep leftover medicines “just in case” or give them to other people.
Tighter controls on the sale of antibiotics
- Strict enforcement: Pharmacies should dispense antibiotics only on prescription.
- Inspections and sanctions: Increased control by government authorities and fines for sales violations.
Raising public awareness
- Information campaigns: National programs to inform the public about the risks of antibiotic resistance.
- Educational programs in schools and universities: Include topics related to the rational use of antibiotics in educational courses.
Reducing the use of antibiotics in agriculture
- Introduction of alternative methods: Use of vaccination, improved animal housing and other disease prevention methods.
- Regulation of antibiotics: Restrict the use of certain classes of antibiotics in livestock production.
Strengthening infection control in health care facilities
- Training of medical staff: Regular trainings on infection prevention and proper use of antibiotics.
- Hygiene compliance: Strict adherence to disinfection and sterilization protocols.
Investments in research
- Developing New Antibiotics: Supporting research and incentivizing pharmaceutical companies to develop new drugs.
- Exploring alternative therapies: Research into bacteriophages, antimicrobial peptides and other innovative approaches.
Conclusion
Antibiotic resistance is a global problem that requires immediate and coordinated action.
In Ukraine, the situation is complicated by a number of specific factors, but we have an opportunity to change the course of events.
Each of us can make a contribution: by following doctors’ recommendations, raising our awareness and responsible attitude to our own health.
It is important to remember that antibiotics are a precious resource that must be protected. Our actions today determine the effectiveness of treatment of infections tomorrow.