Gene-based vaccines are one of the most innovative and promising areas in modern medicine.
They open up new opportunities in the fight against infectious diseases and cancer.

In this article, we will look at what gene vaccines are, their advantages and disadvantages, and the prospects for their use.

What are gene vaccines
Gene vaccines are preparations containing the genetic material (DNA or RNA) of a pathogen that stimulates the body’s immune response without using the pathogen itself.
When such a vaccine is introduced into the body, cells begin to produce specific proteins recognized by the immune system, which provides protection against the disease.
Benefits of gene vaccines
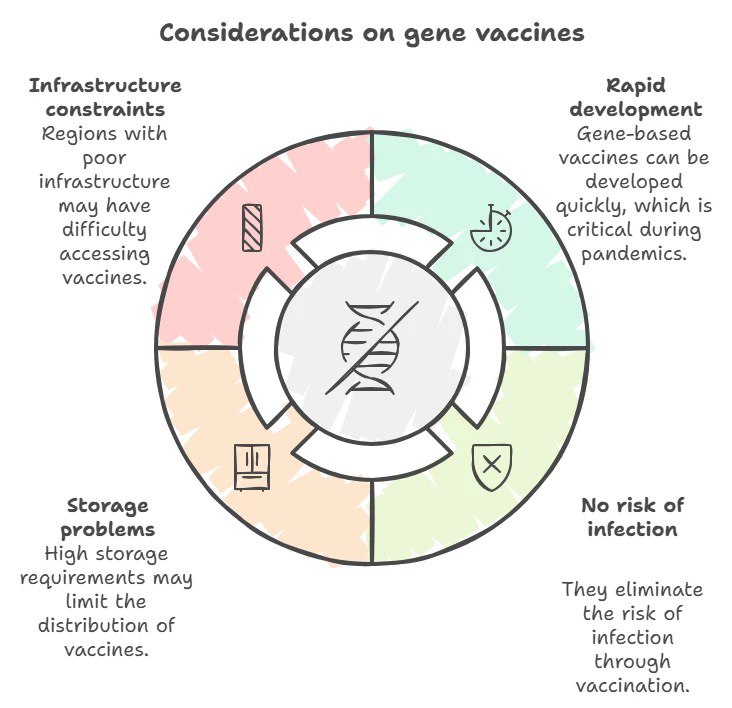
- Rapid development: The use of genetic material makes the vaccine development process much faster.
- Safety: The absence of live components reduces the risk of infection from the vaccine itself.
- Strong immune response: Stimulation of both humoral and cellular immunity provides more effective protection.

Use of gene vaccines
COVID-19
The best known example of gene vaccines are the mRNA vaccines against COVID-19 from Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna.
These vaccines have shown high efficacy and safety in clinical trials and are widely used worldwide.
Oncology
Gene vaccines are also being investigated to treat different types of cancer. They can stimulate the immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells.
Disadvantages and Challenges
- Storage and transportation: Some gene vaccines require ultra-low storage temperatures, making distribution difficult.
- Immunogenicity: The possibility of strong immune reactions requires careful monitoring.
- Long-term efficacy: Additional studies are needed to assess the duration of the protective effect.

Development prospects
Gene-based vaccines have great potential in the treatment of various diseases. The development of genetic material delivery technologies and improvement of vaccine stability will expand their use in medicine.
Table 1: Comparison of traditional and gene vaccines
| Criterion | Traditional vaccines | Gene vaccines |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Weakened/inactivated pathogens | DNA or RNA of the pathogen |
| Risk of infection | Low | Absent |
| Storage conditions | Standard | May require low temperatures |
| Development time | Prolonged | Quick |
Looking at Table 1, there are significant differences between traditional and gene vaccines.
The main advantage of gene vaccines is their speed of development and lack of risk of infection, which is particularly important in pandemics and rapidly spreading diseases.
However, as the table shows, gene-based vaccines have higher storage requirements, which can be an obstacle to their widespread distribution, especially in regions with limited infrastructure.
Table 2: Examples of gene vaccines in development
| Disease | Vaccine type | Development phase, Organization |
|---|---|---|
| COVID-19 | mRNA | Uses, Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna |
| HIV | DNA | Clinical Trials, Inovio Pharmaceuticals |
| Prostate cancer | DNA | Preclinical Research, Johns Hopkins University |
Conclusion
Gene-based vaccines represent a revolutionary step in medicine, offering new methods of disease prevention and treatment.
Despite the current challenges, their development promises a significant impact on global health.
List of references
- Polack, F. P., et al. (2020). Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. The New England Journal of Medicine, 383(27), 2603-2615.
- Jackson, L. A., et al. (2020). An mRNA Vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 — Preliminary Report. The New England Journal of Medicine, 383(20), 1920-1931.
- Liu, M. A. (2019). A Comparison of Plasmid DNA and mRNA as Vaccine Technologies. Vaccines, 7(2), 37.