The importance of the spine to overall health
The spine is not only the main support of our body, but also an essential component of the nervous system.
It protects the spinal cord, which is responsible for transmitting signals between the brain and the rest of the body.
A healthy spine provides flexibility, mobility and maintains good posture, which is important for performing everyday tasks.
As we age, there are natural changes in the structure of the spine, such as degradation of the intervertebral discs and a decrease in bone density.
After the age of 35, many people begin to experience back pain and discomfort, which can be related to factors such as sedentary lifestyles, poor posture, stress, and injuries.
These problems not only impair quality of life, but can also lead to serious complications, including decreased mobility, chronic pain, and impaired internal organ function.
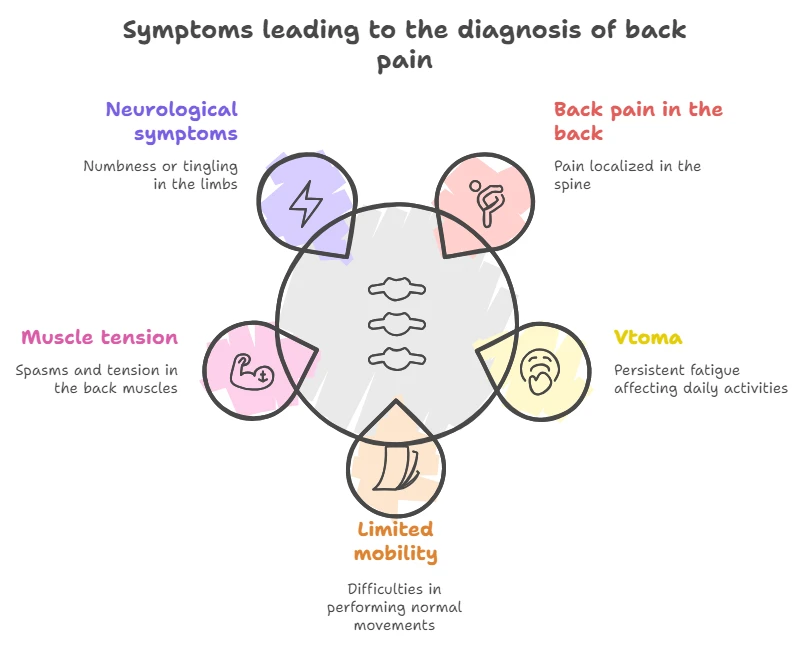
Symptoms of spinal problems
Spinal problems can manifest with a variety of symptoms that vary in intensity and localization. The main signs include:
- Back pain: May be acute or chronic, localized in the cervical, thoracic or lumbar spine.
- Fatigue: Constant fatigue may be due to strained back muscles that compensate for spinal dysfunction.
- Limited mobility: Reduced flexibility of the spine makes it difficult to perform normal movements such as bending or turning.
- Severe muscle tightness: Muscle spasms and tension often accompany back pain.
- Neurological symptoms: Numbness, tingling or weakness in the extremities may indicate nerve root compression.
Early diagnosis and timely referral to specialists can help avoid worsening of the condition and the development of chronic diseases.
Types of spinal disorders
There are many diseases of the spine, each of which has its own characteristics and methods of treatment. Let us consider the main ones in more detail:
Main types of spinal disorders
| type of disease | characteristics |
|---|---|
| osteochondrosis | disc degeneration, vertebral pain. |
| disc herniation | disc out of the vertebrae, leg pain |
| spondyloarthritis | joint inflammation of the vertebrae |
| vertebral instability | Spinal structure and function disorders, subluxations |

Osteochondrosis
Description: Osteochondrosis is a degenerative disease of intervertebral discs and vertebrae, accompanied by a decrease in their height and changes in structure. This leads to impaired cushioning and mobility of the spine.
Symptoms:
- Lower back or neck pain
- Limitation of mobility
- Muscle spasms
Treatment: Includes physiotherapy, medication, exercises to strengthen the back muscles and, in severe cases, surgery.
Herniated disk
Description: A herniated disc occurs when an internal gel-like substance extends beyond the fibrous ring, compressing nerve roots and causing pain.
Symptoms:
- Sharp pain that irradiates to the extremities
- Numbness and tingling
- Muscle weakness
Treatment: Conservative methods include physical therapy, medications and injections. In cases of severe nerve compression, surgical removal of the herniated disc may be necessary.
Spondyloarthritis
Description: Spondyloarthritis, an inflammatory disease of the joints of the spine, is often associated with conditions such as ankylosing spondylitis.
Symptoms:
- Chronic pain and stiffness
- Limitation of spinal mobility
- Joint inflammation
Treatment: Includes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), physical therapy and, in some cases, biologics.

Vertebral instability
Description: Vertebral instability is characterized by disruption of the normal structure and function of the spine, which can lead to subluxations and poor posture.
Symptoms:
- Chronic pain
- Spinal instability
- Posture disorders
Treatment: Includes the use of orthopedic braces, physical therapy and surgery to restore stability to the spine.

Methods of diagnosing the spine
Accurate diagnosis of spinal diseases requires a comprehensive approach and the use of various methods of examination. Let’s consider the main ones:
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Description: MRI provides detailed images of soft tissues, including intervertebral discs, nerves and spinal cord. It is the most informative method for diagnosing herniated discs, osteochondrosis and other degenerative changes.
Advantages:
- High accuracy
- No ionizing radiation
Computerized tomography (CT).
Description: CT is used for detailed examination of the bony structures of the spine. This technique is particularly useful in the evaluation of fractures, degenerative changes, and anatomical anomalies.
Advantages:
- High bone detail
- Fast procedure
Radiography
Description: X-ray allows you to assess the general condition of the spine, identify vertebral misalignments, changes in their shape and structure. It is a basic diagnostic method, often used at the initial stages of examination.
Advantages:
- Affordability
- Quickness of implementation
Additional methods
- Electromyography (EMG): Evaluates nerve and muscle function and can help detect nerve root compression.
- Bone biopsy: Performed when tumors or infections of the spine are suspected.
Who do I turn to for help?
If back pain occurs, it is important to see a doctor in time to receive qualified help. The primary specialist to see is a general practitioner. He or she will make an initial assessment of your health and, if necessary, refer you to specialized specialists:
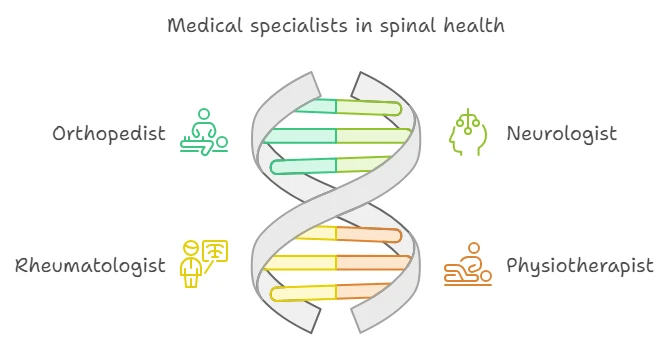
- Orthopedist: Specializes in diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
- Neurologist: Diagnoses and treats neurological complications of spinal disorders.
- Rheumatologist: Deals with inflammatory diseases of the spine such as spondyloarthritis.
- physiotherapist: Develops a set of exercises to rehabilitate and strengthen the back muscles.
It is also important to consider a multidisciplinary approach when treating complex diseases. For example, in spondyloarthropathy, “the patient needs the support of specialists from different fields of medicine” (Tetiana Ankeeva).
The impact of lifestyle on spinal health
Lifestyle plays a key role in maintaining a healthy spine. Improper habits and lack of physical activity can significantly increase the risk of developing spinal conditions.
Main risk factors
| risk factor | spinal effect |
|---|---|
| bad posture | increases the strain on the spine |
| immobility | leads to a weakening of the muscular corset. |
| improper diet | Nutrient deficiencies weaken bone tissue |
| stress | can cause muscle spasms and worsen back conditions |
| injuries | cause spinal and muscle injuries |
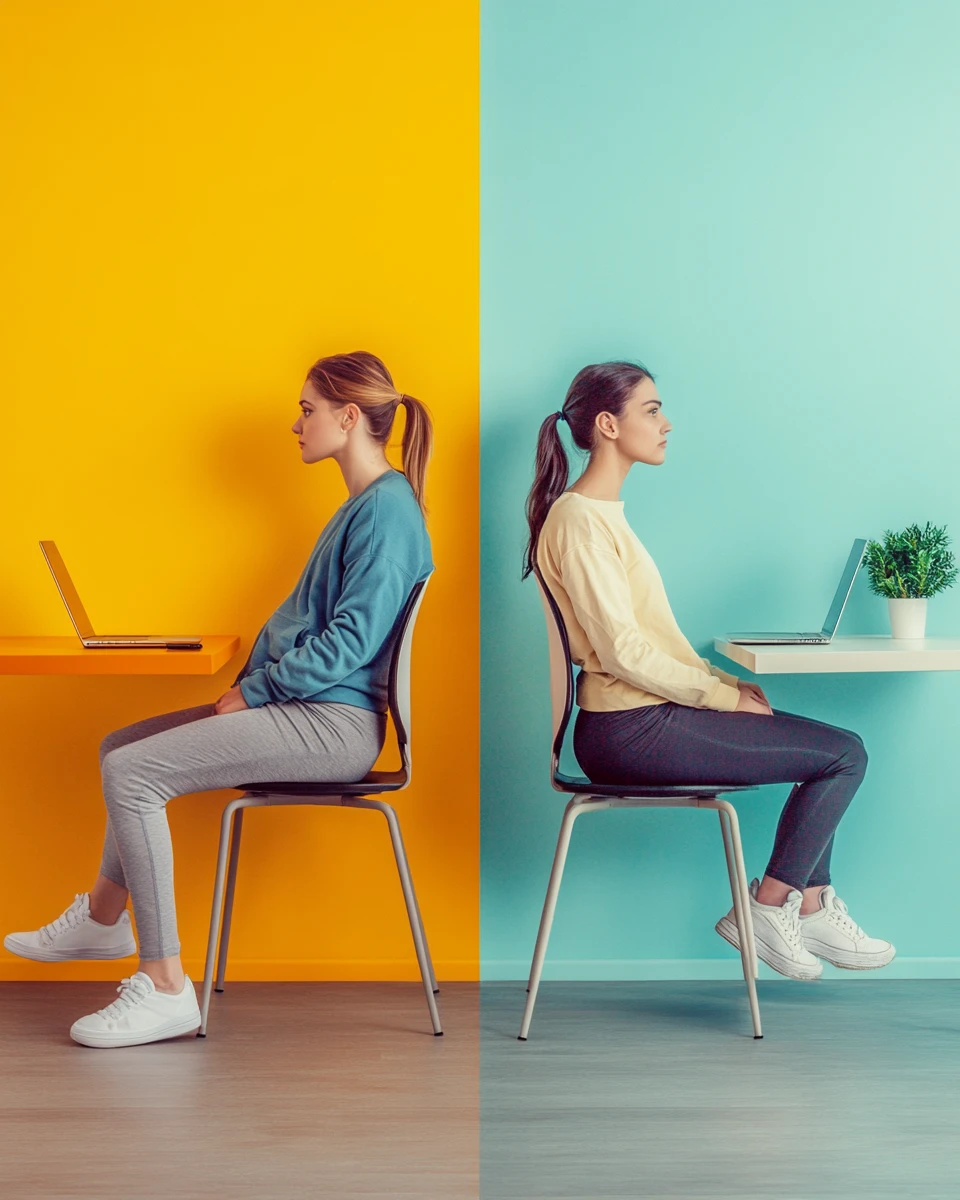
Improper posture
Description: Prolonged exposure to an incorrect posture, such as sitting at a computer with a slouching back, puts excessive strain on the intervertebral discs and back muscles.
Consequences:
- Deterioration of the discs
- Muscle spasms and pain
- Posture disorders
Recommendations:
- Maintain an ergonomic posture when working
- Take regular breaks and perform stretching exercises
Sedentary lifestyle
Description: Lack of physical activity leads to weakening of the muscular corset that supports the spine and promotes degenerative changes.
Consequences:
- Decreased flexibility and mobility
- Increased strain on the spine
- Increased risk of injury
Recommendations:
- Regular exercise, including cardio and strength training
- Incorporating stretching and flexibility exercises into the daily regimen
Improper nutrition
Description: Deficiencies in essential nutrients such as calcium and vitamin D can lead to decreased bone density and weakened bone tissue.
Consequences:
- Osteoporosis
- Increased risk of fractures
- Deterioration of intervertebral discs
Recommendations:
- A balanced diet with adequate calcium and vitamin D content
- Consumption of foods rich in protein and other vitamins
- Avoid excessive salt and sugar intake

Recommendations for spinal health
The following guidelines should be followed to maintain a healthy spine and prevent disease:
Physical exercise
Regular exercise strengthens the back and cortical muscles, increases flexibility and improves posture. Recommended:
- Yoga and Pilates: Stretch and strengthen muscles.
- Cardio: Improves circulation and overall body condition.
- Strength training: Strengthen the muscular corset that supports the spine.
Maintaining good posture
Proper posture reduces stress on the spine and prevents the development of back pain.
Recommendations:
- Monitor back posture when sitting and standing
- Use ergonomic furniture
- Avoid staying in one position for long periods of time
Avoiding overload
Heavy exercise and improper weight lifting can lead to spinal injuries.
Recommendations:
- Lift objects correctly: bend your knees, keep your back straight
- Divide heavy loads into several stages
- Use special devices for carrying heavy things

Balanced nutrition
Proper nutrition helps strengthen bones and maintain healthy intervertebral discs.
Recommendations:
- Consume adequate amounts of calcium and vitamin D
- Include foods rich in protein, vitamin C and other essential vitamins in your diet.
- Avoid excessive salt and sugar intake
Regular medical examinations
Periodic visits to your doctor can help detect problems early and prevent them from developing.
Recommendations:
- Get regular checkups, especially if you have risk factors
- Seek help promptly if you have pain or other symptoms
Stress management
Chronic stress can lead to muscle spasms and spinal deterioration.
Recommendations:
- Practice relaxation techniques such as meditation and breathing exercises
- Engage in hobbies and spend time outdoors
- Maintain social ties and seek psychological support when needed
Conclusion:
Following these recommendations will help maintain spine health, improve quality of life and avoid serious complications.
Remember that timely prevention and seeking professional help are key factors in maintaining the health of your spine.