In recent years, vitamin D has attracted increasing attention not only as a regulator of bone metabolism, but also as a powerful modulator of the immune system.
Deficiency of this vitamin is associated with an increased risk of various autoimmune diseases, including psoriasis, vitiligo and systemic lupus erythematosus.

Biological role of vitamin D
Vitamin D is synthesized in the skin by ultraviolet radiation and converted to its active form, calcitriol, in the liver and kidneys.
Calcitriol interacts with vitamin D receptors (VDRs), which are present in many cells of the body, including immune cells.
Interesting fact: More than 80% of the Ukrainian population is deficient in vitamin D, especially during the winter months.
Effect of vitamin D on the immune system
Vitamin D plays a key role in regulating innate and adaptive immunity.
It is able to modulate the activity of various immune cells, reducing the risk of autoimmune reactions.
Table 1: Effect of vitamin D on immune cells
| Immune cells | Effect of vitamin D |
|---|---|
| T-helper cells (Th1 and Th17) | Suppression of proliferation and differentiation |
| Regulatory T cells | Stimulation of development and function |
| Dendritic cells | Decreased antigen presentation |
| B-cells | Regulation of antibody production |

Vitamin D and autoimmune diseases
Psoriasis
Vitamin D is used in psoriasis therapy due to its ability to inhibit keratinocyte proliferation and modulate the immune response.
Topical preparations based on vitamin D have shown high efficacy in reducing the symptoms of the disease.
Vitiligo
What is vitiligo?
Vitiligo is a chronic skin disease in which areas of depigmentation, i.e. white patches of various shapes and sizes, appear on the skin.
These patches are caused by the destruction or decreased activity of melanocytes, the cells responsible for the production of melanin, the pigment that gives skin, hair and eyes their natural color.
The exact cause of vitiligo is not fully understood, but it is believed to be based on autoimmune processes in which the immune system mistakenly attacks its own melanocytes.
The role of vitamin D in vitiligo
Research suggests that vitamin D may play a significant role in vitiligo therapy.
Due to its immunomodulatory properties, vitamin D is able to reduce autoimmune activity directed against melanocytes.
In addition, it stimulates the processes of melanogenesis – melanin synthesis, which helps to restore the skin’s natural pigmentation.
Interesting Fact: In one clinical trial, the use of a topical vitamin D analog, calcipotriol, in combination with phototherapy resulted in significant improvement in skin conditions in patients with vitiligo.
Mechanisms of vitamin D action in vitiligo:
- Immunomodulation: Vitamin D inhibits the activity of T-helper type 1 (Th1) and cytotoxic T-lymphocytes, which are involved in the destruction of melanocytes.
- Melanocyte stimulation: It promotes proliferation and differentiation of melanocytes, increasing melanin synthesis.
- Antioxidant action: Vitamin D reduces oxidative stress in the skin, which can damage melanocytes.

Clinical research and therapeutic approaches:
- Topical therapy: Application of creams and ointments containing vitamin D or its analogs can stimulate repigmentation in the affected areas.
- Systemic therapy: Oral vitamin D supplements may be used as an adjunctive therapy for vitiligo.
- Combination therapy: Combining vitamin D with phototherapy (UV irradiation) enhances the therapeutic effect due to synergistic action on melanocytes.

Practice Guidelines:
- Vitamin D level monitoring: Patients with vitiligo are recommended to regularly check the level of vitamin D in the blood.
- Correction of deficiency: If deficiency is detected, correction is necessary by prescribing appropriate doses of vitamin D under medical supervision.
- Integrated approach: Effective treatment of vitiligo requires an individualized approach and may include a combination of drug therapy, phototherapy and lifestyle changes.
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Vitamin D deficiency is associated with increased activity of systemic lupus erythematosus . Vitamin D supplementation can reduce disease activity and improve patients’ quality of life.
Clinical studies and perspectives
A number of clinical studies confirm the positive effects of vitamin D on the course of autoimmune diseases.
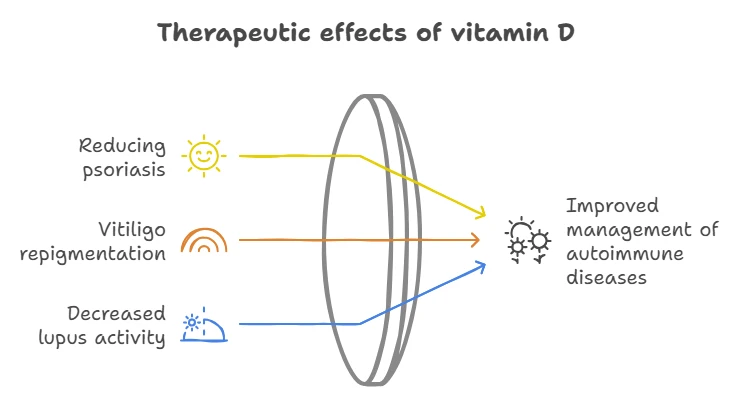
Table 2: Clinical trials of vitamin D in the therapy of autoimmune diseases
| Disease | Results of the study | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Psoriasis | 48% reduction in skin lesion area | [2] |
| Vitiligo | Increased repigmentation by 25% | [3] |
| Systemic lupus erythematosus | Decrease in disease activity according to the SLEDAI index | [4] |

Recommendations and conclusion
Given the importance of vitamin D in immune regulation, regular monitoring of its levels in patients with autoimmune diseases is recommended.
Correction of vitamin D deficiency may become an important part of complex therapy.
List of references
- Holick MF. Vitamin D deficiency. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(3):266-281.
- Morimoto S, Kumahara Y. A patient with psoriasis cured by 1 alpha-hydroxyvitamin D3. Med J Osaka Univ. 1985;35(3-4):51-54.
- Saleh HM, Abdel Fattah NS, Zaki NS. Evaluation of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels in vitiligo patients. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2013;29(1):34-40.
- Abou-Raya A, Abou-Raya S, Helmii M. The effect of vitamin D supplementation on disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72(4):626-629.